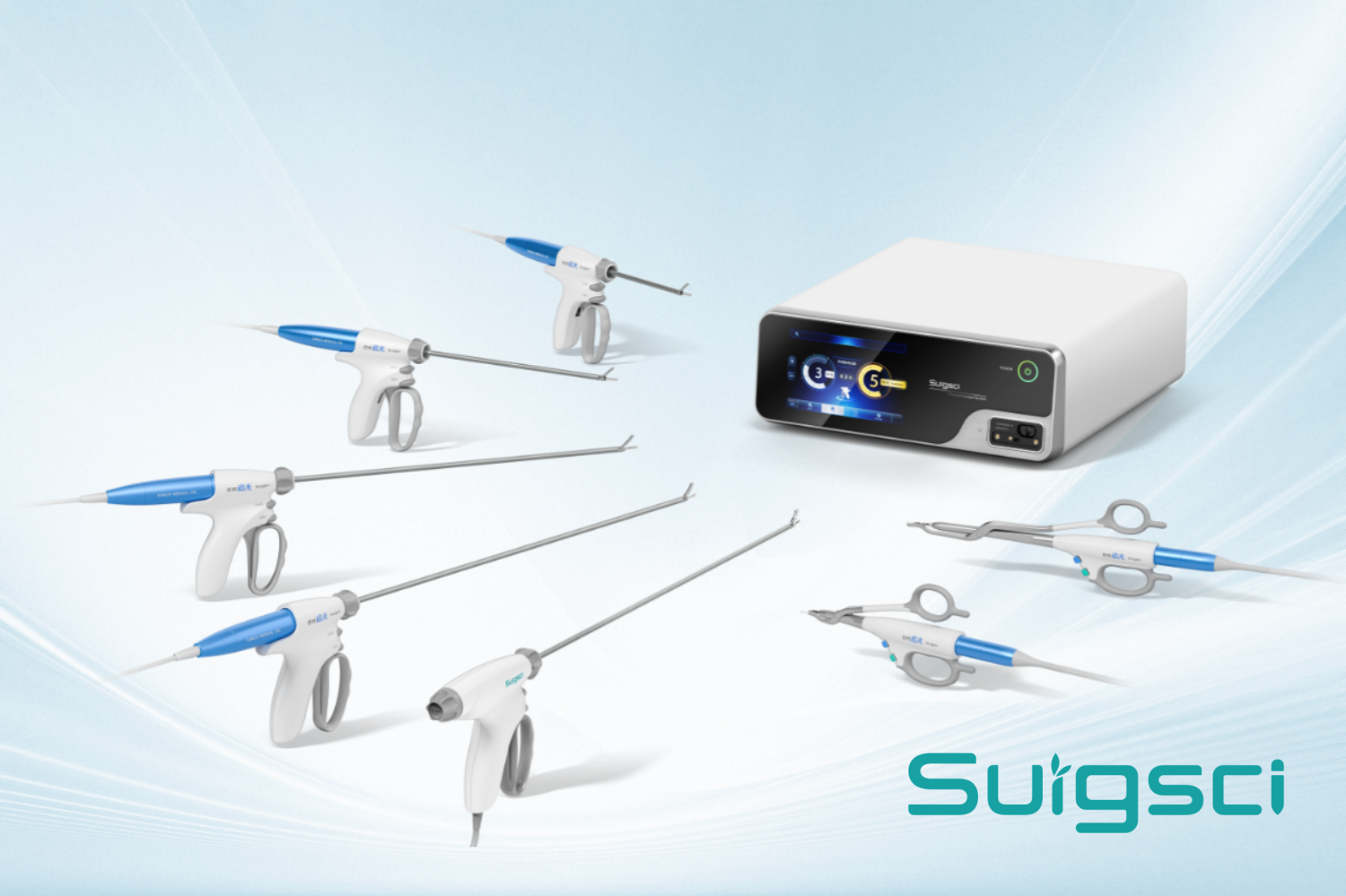
With the improvement of medical technology and the gradual change of national medical concepts, minimally invasive surgery is accepted by more and more patients. The advantages of minimally invasive surgery are short operation time, less trauma, and quick postoperative recovery, which not only reduces the pain of patients, but also improves the overall medical efficiency. Surgical instruments with excellent hemostasis and sealing capabilities are essential instruments for every minimally invasive surgery.
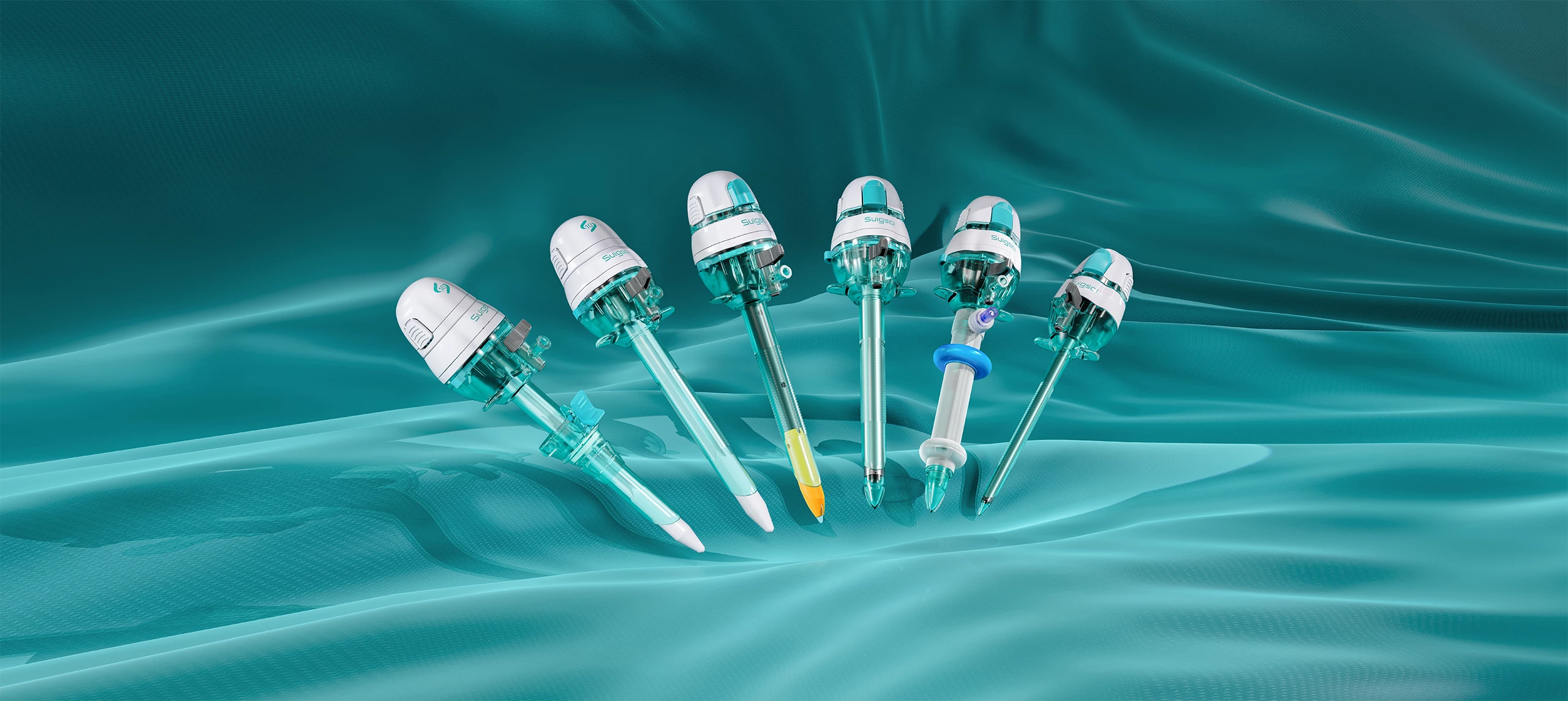
Ligation clips are a kind of instrument that plays a vital role in surgical operations. They are used to close tissues or blood vessels, control bleeding, and prevent fluid leakage. The following is a detailed classification of ligation clips:
Classification by Material:
- Metal Titanium Ligating Clips: Typically made from titanium or stainless steel, these clips have good biocompatibility and are less likely to cause adverse reactions. They are commonly used for permanently ligating important blood vessels when long-term implantation is necessary.
- Absorbable Ligating Clips: Made from materials that gradually absorb in the human body (such as polyglycolic acid or polylactic acid), these clips are suitable for temporarily closing tissues or blood vessels. After a certain period post-surgery, the clips naturally degrade and are eliminated from the body.
- Non-absorbable Ligating Clips: Similar to metal clips, these may also be made from other biocompatible materials. They are not absorbed by the body and are suitable for long-term closures.
Classification by Application Method:
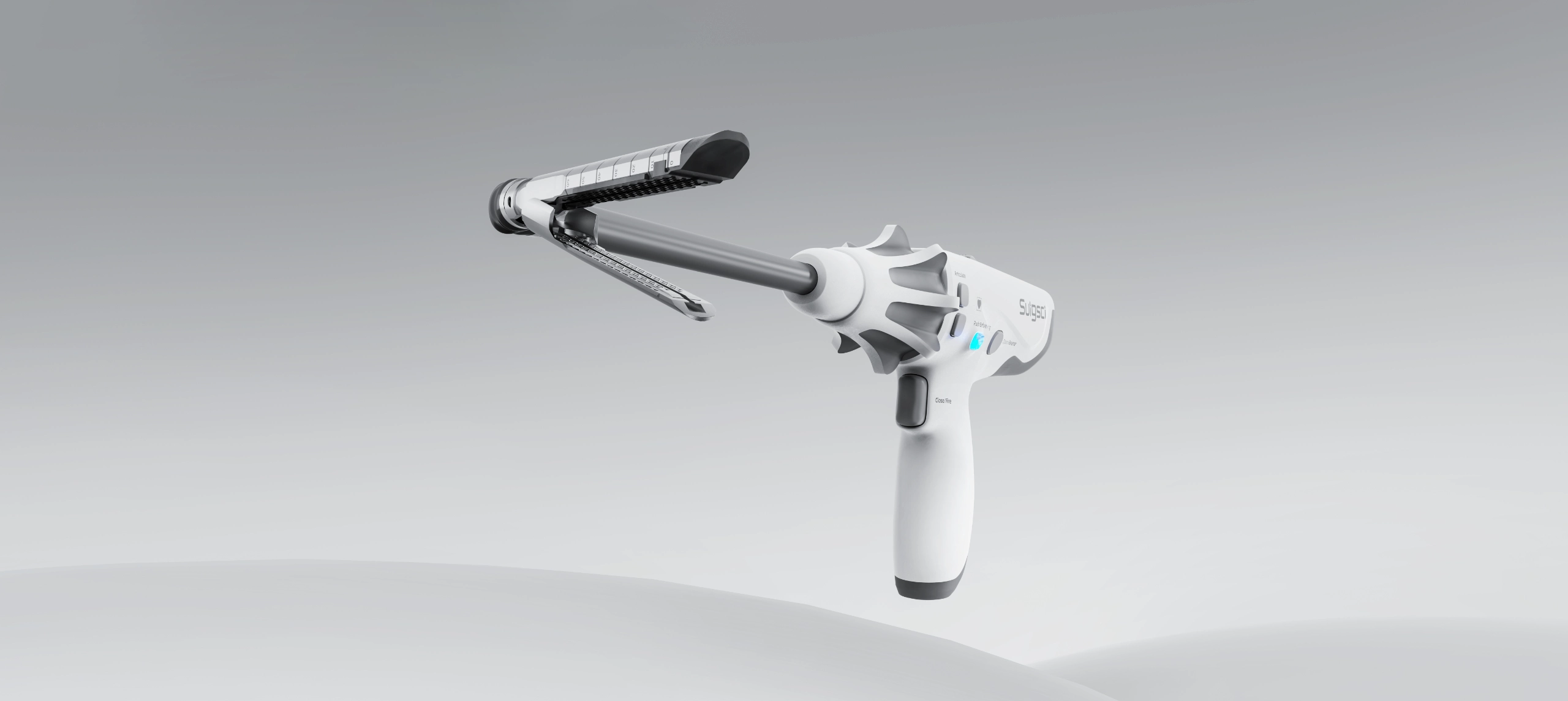
- Single-Use Ligating Clips: These allow precise control over the number and location of clips applied. They are commonly used in surgeries requiring high precision.
- Continuous-Use Ligating Clips: These clips can be consecutively applied using specialized applicators, making them suitable for scenarios where rapid and numerous closures are needed, thus improving surgical efficiency.
Differences in Activation Methods
From a patient’s perspective in clinical practice, whether using single-fire or multi-fire ligating clips, the intended purpose is almost the same. However, the clinical price for single-fire clips is typically in the tens of yuan, while multi-fire clips can cost over a thousand yuan, resulting in a significant price difference. Despite being available for many years, multi-fire ligating clips are still used very infrequently in clinical settings, primarily due to considerations related to patient treatment costs.
Current State of Absorbable Clips
Both absorbable clips and non-absorbable polymer or titanium clips offer significant benefits to patients in clinical applications. Absorbable clips are typically absorbed within approximately 6 months after implantation, leaving no residue in the patient’s body. However, due to mechanical performance issues associated with absorbable clips, their clinical use requires caution. Specifically, the degradation time is difficult to precisely control, and uneven degradation within the body can lead to serious clinical incidents, such as excessive bleeding.
Additionally, because absorbable clip materials are relatively soft, doctors cannot hear a distinct “click” sound during the clamping procedure, resulting in a stronger sense of uncertainty and insecurity. Compared to non-absorbable clips, absorbable clips have expensive raw material costs. For patient safety reasons, it is expected that clinical use will continue to rely heavily on long-term implantable polymer clips over the next 5 years. However, we believe that with ongoing advancements in absorbable polymer material technology, absorbable clips will see widespread clinical adoption in the future.